What is Darwinia Network? Cross-chain transfers made easy

Darwinia Network enables the connection of different blockchain via its cross chain technology. As a result, many call it the bridge blockchain given that it also connects to the Polkadot Network as a para-chain. Darwinia aims to solve the lone wolf concept that has been plaguing several DeFi platforms. Initially, the concept of smart contracts and blockchains were to make them do all the operations themselves.
This seemed to be the most secure choice, but developers quickly realized that by having no significant communication with other chains then you are limiting potential. If blockchains could easily work together, then overally the crypto ecosystem offers more value while becoming stronger. Many teams are working on cross chain interoperability solutions, here we will look at one of Polkadot’s offerings: Darwinia.
In this article we will review Darwinia Network cross chain solution, staking tokenomics, ID system. And also the RING and KTON tokens.
What is Darwinia Network?
Darwinia Network is powered by a Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm, which like Polkadot or Dock is built using the Substrate network. The goal is to enable the cross chain transfer of any crypto assets such as tokens or collectibles. Darwinia also looks to power decentralized exchanges for trades and swaps across different blockchains. The platform will exist as a para-chain of Polkadot, but if needed, it can operate in solo mode.
For the moment, the major applications built on Darwinia focus on the gaming and DeFi space of cryptocurrency. Darwinia features an Appchain SDK which allows developers to build dApps without the need to know smart contract languages. As a result, onboarding and adoption for teams to start building on the mainnet will be fairly easy.
RING
RING is the native utility token found on the network, used for all operations. The token’s primary use is to pay for transactions when sending assets, or interacting with dApps on the network.
Developers will also need RING to deploy new contracts or use storage for their applications. RING follows an inflationary model, where new tokens are minted via a staking mechanism.
KTON
KTON is an incentive for holders to stake RING tokens. When you stake RING for a period of 3 to 36 months, then KTONs generate passively as rewards. You can draw similarities with KTON and liquidity minint programs on DeFi platforms. However, here KTON is more a compensation for the liquidity loss (locking up your RING). Each staker receives KTON in proportion to the amount of RING staked. There is also a bonus for duration, the longer you hodl, the more KTON you will receive.

KTON can only be minted when RING is locked, meaning that the initial supply is zero. For the moment, details around KTON’s use cases have not been released. We expect it to be a requirement for registering Dapps or other projects as an official application on the Darwinia Network.
How does staking in Darwinia work?
Both RING and KTON tokens can be staked to earn rewards and benefits. However, to earn KTON tokens, users have to agree to a minimum lock up period of 3 months. You can choose a longer period to earn more rewards. During the locking period, users cannot withdraw their RING tokens.
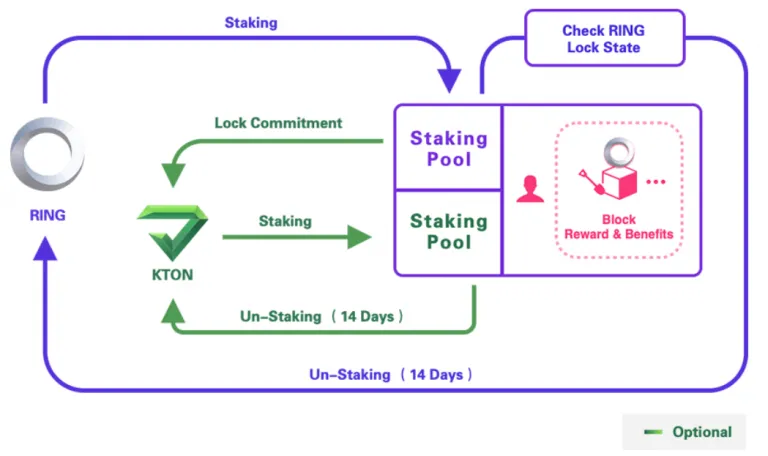
Unless you are happy to pay a hefty penalty fee, which is three times your potential KTON earnings, then you can unlock your RING tokens early. Once you have earned KTON rewards, it is possible to stake these tokens to earn additional staking power.
Darwinia mainnet launch is scheduled to happen between September 25th and October 15th. Once the mainnet is live, we will have more details on expected returns and rewards for RING stakers.
Darwinia ID
As a network aiming to facilitate cross chain trading, Darwinia needs a way to identify the same assets on multiple blockchains. Enter Darwinia ID, which aims to tag and develop a standardized database for different crypto assets. Technically called Interstellar Product Coding Standard, it works by giving a single identifier code to assets on multiple blockchains. This ensures users can easily make cross chain transfers without a major loss of value when executing the trade.
What is Darwinia Network in the future?
Darwinia will likely start a new era of cross chain asset transfers when the mainnet goes live by the end of Q3 2020. There are hundreds of use cases for the migration of DeFi assets and NFTs (collectibles) across multiple blockchains, and teams will be eager to leverage Darwinia’s technology.
Furthermore, Darwinia is part of the Polkadot ecosystem, which continues to gain more traction as Ethereum transaction fees rise beyond sustainable levels. Watch the mainnet launch closely!
